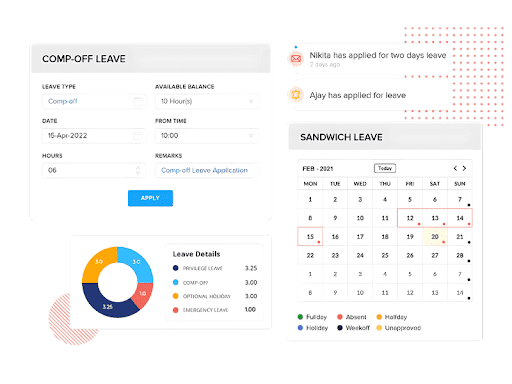
Absence tracking is a crucial aspect of effective human resource management, allowing organizations to monitor and manage employee attendance, sick days, vacations, and other forms of absence. By implementing absence tracking systems, companies can improve operational efficiency, ensure compliance with labor laws, and maintain a clear understanding of workforce availability. Accurate absence records also help in making data-driven decisions, minimizing productivity loss, and fostering a supportive work environment.
Understanding Employee Absence Tracking
Absence tracking refers to the ongoing process of documenting and analyzing instances when employees are not present at work. This includes:
Planned Absences – Such as vacations, pre-approved personal leave, or medical appointments.
Unplanned Absences – Unexpected time off due to illness, family emergencies, or other urgent matters.
Paid Absences – Time away from work that still qualifies for compensation, like vacation days or statutory holidays.
Unpaid Absences – Days off that exceed the allocated leave or are taken without pay.
Statutory Absences – Leave types mandated by law, such as jury duty or maternity/paternity leave.
The core objective of tracking absences is to maintain accurate records for payroll, legal compliance, workforce planning, and performance assessment.
Key Aspects of Employee Absence Tracking
Employee absence tracking is the process of recording and analyzing instances when employees are absent from work. It’s essential for workforce planning, legal compliance, and performance management. The following categories of absences should be tracked:
| Type of Absence | Description |
|---|---|
| Planned Absences | Scheduled time off such as vacations, medical appointments, or pre-approved personal leave. |
| Unplanned Absences | Unexpected time off due to illness, family emergencies, or other unforeseen circumstances. |
| Paid Absences | Time off that is compensated, such as vacation days, public holidays, or sick leave. |
| Unpaid Absences | Time taken off without pay, typically when the leave balance is exhausted. |
| Statutory Absences | Leave mandated by law, such as maternity/paternity leave or jury duty. |
Tracking absences helps maintain accurate payroll records, comply with legal requirements, and make informed workforce planning decisions.
Tracking Duration and Impact
Tracking the duration of each absence is essential for understanding its impact on the organization. By documenting whether the absence is short-term (e.g., a day off) or long-term (e.g., extended medical leave), HR managers can assess how absences affect staffing levels and plan accordingly. Long-term absences may require temporary replacements or adjustments to workloads to minimize disruptions.
Analyzing Absence Patterns
A key advantage of absence tracking is the ability to analyze absence trends over time. By monitoring employee attendance data, HR managers can identify recurring issues, such as frequent unplanned absences from a particular employee, or broader trends affecting an entire department or organization. Identifying patterns allows organizations to take proactive steps to address the underlying causes, whether related to health, job satisfaction, or other factors.
Importance of Absence Tracking
Effective absence tracking offers several benefits that contribute to the overall success and well-being of the organization:
1. Maintaining Productivity
Absenteeism can significantly impact productivity, especially in smaller teams or critical roles. By tracking absences, organizations can plan for potential disruptions, redistribute workloads, and avoid productivity loss. When absences are anticipated and managed efficiently, organizations can maintain steady workflows and minimize bottlenecks.
2. Ensuring Legal Compliance
Various labor laws and regulations govern employee leave entitlements, including sick leave, vacation time, and family leave. Inaccurate or incomplete absence records can result in legal penalties and employee disputes. By maintaining accurate and up-to-date absence records, organizations ensure compliance with relevant laws, reducing the risk of legal issues.
3. Supporting Employee Well-being
Absence tracking does more than manage time off; it can also highlight potential employee health or morale issues. For example, frequent or prolonged absences might signal underlying physical or mental health challenges. By monitoring absence trends, organizations can provide necessary support to employees, such as access to health resources, counseling, or flexible work arrangements.
4. Improving Resource Planning
Absence tracking also plays a critical role in resource planning. By analyzing absence patterns, HR managers can better anticipate staffing needs and prepare for peak periods. Effective tracking enables organizations to allocate resources efficiently, ensuring that there is always adequate coverage during planned and unplanned absences.
5. Cost Reduction
Absenteeism has a direct financial impact on organizations. A report from the CDC estimated that absenteeism costs U.S. employers $225.8 billion annually due to lost productivity. With robust absence tracking systems, organizations can reduce absenteeism rates, minimize unnecessary costs, and improve overall operational efficiency.
Best Practices for Absence Tracking
To maximize the effectiveness of absence tracking, organizations should adopt a set of best practices:
1. Establish Clear Attendance Policies
A clearly defined attendance policy provides employees with a framework for understanding acceptable and unacceptable reasons for absence, the process for requesting leave, and the consequences for unauthorized absences. Clear policies set expectations, reduce misunderstandings, and foster transparency within the organization.
2. Implement Automated Tracking Systems
Manual tracking can be prone to errors and can consume significant time and resources. Automated absence tracking systems eliminate human error and reduce administrative workload by automatically recording absences, updating leave balances, and generating reports. Automation streamlines the process, providing HR teams with more time to focus on strategic tasks.
3. Regularly Review Absence Data
Absence data should be reviewed on a regular basis to identify patterns, trends, and areas of concern. For example, if one department experiences high absenteeism, HR may want to investigate the cause—whether it’s workload, job satisfaction, or something else—and take corrective action. Regular data review also enables organizations to track the effectiveness of their absence management strategies.
4. Maintain Confidentiality
It’s essential to protect employee privacy when handling absence data. Attendance records, especially those related to medical or personal leave, should be kept confidential to respect employees’ rights. Ensure that absence data is stored securely and shared only with authorized personnel to maintain confidentiality and trust.
5. Provide Support for Frequent Absentees
Frequent absences may indicate underlying health issues, burnout, or dissatisfaction with work. Offering support to employees with frequent absences—such as flexible working hours, counseling, or wellness programs—can help address the root causes and improve overall employee retention and engagement.
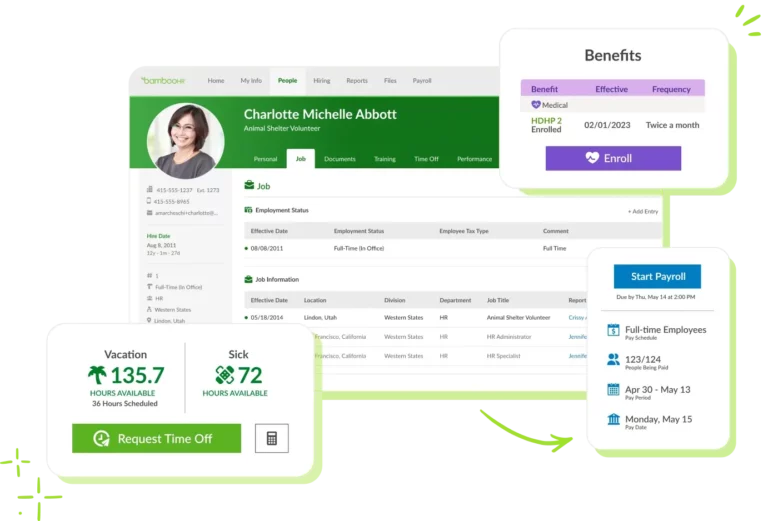
Day Off Vacation Tracker is an innovative tool designed to streamline the way organizations track and manage employee absences. With its user-friendly interface and comprehensive features, it offers both employees and HR departments an efficient, transparent, and flexible approach to handling time-off requests. Here’s a closer look at the features and benefits of using Day Off for employee absence management:
Key Features of Day Off
Day Off is designed to simplify employee absence management. With a range of features that streamline the leave request and approval process, it allows HR teams and managers to efficiently track and manage employee absences, improving workflow, compliance, and transparency across the organization. Let’s explore some of its standout features.
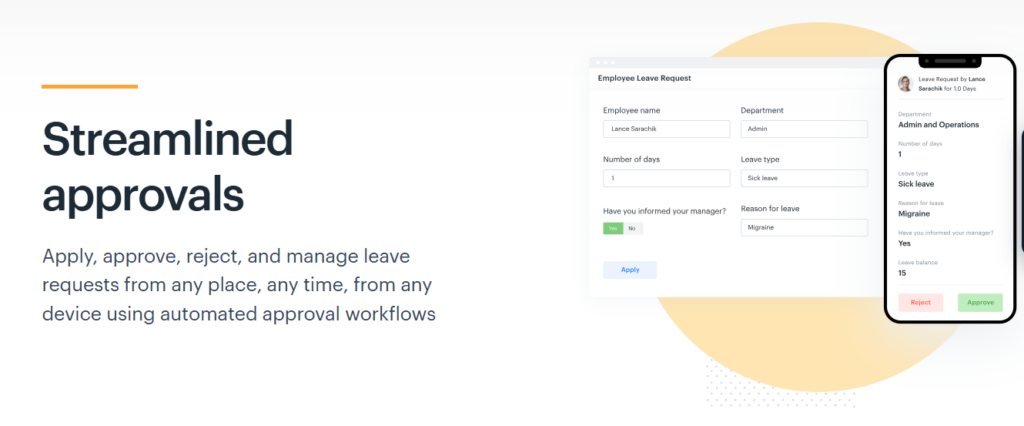
1. Effortless Leave Requests and Approvals
Day Off simplifies the process of requesting and approving leave. Employees can submit their leave requests directly through the platform, selecting the type of leave they need (e.g., vacation, sick leave, personal day). The process is quick and intuitive, requiring only a few clicks.
For managers, Day Off provides a clear overview of all pending requests, enabling them to approve or deny leave requests in real time, reducing delays and ensuring smooth operations. Automated notifications alert both employees and managers when a request has been submitted, approved, or denied, minimizing communication errors.
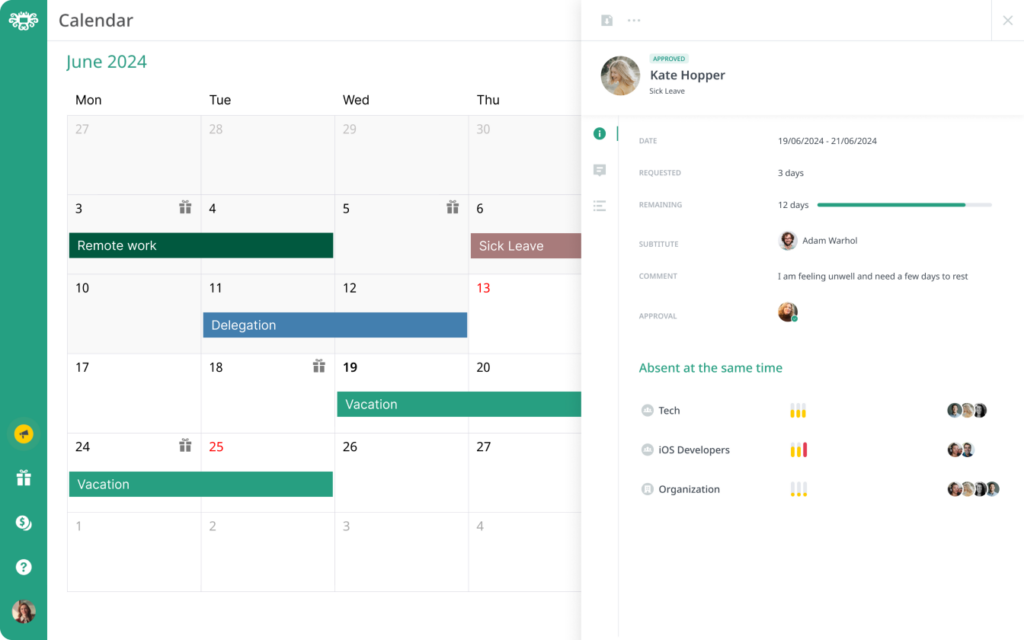
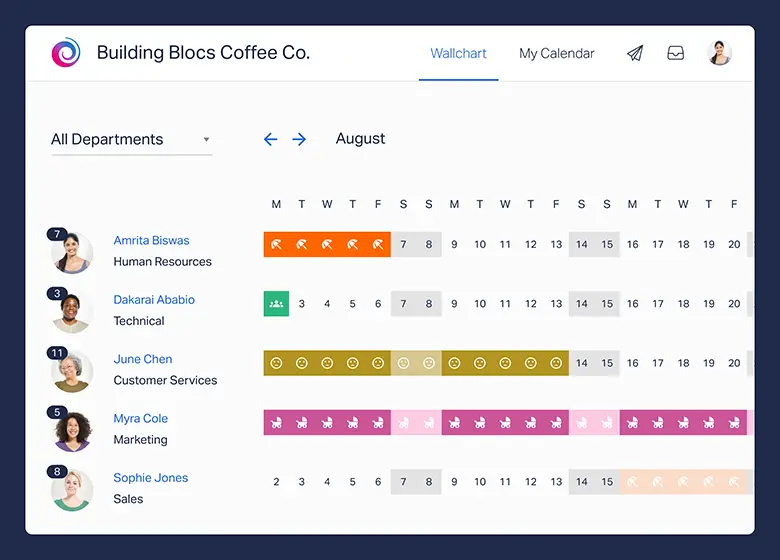
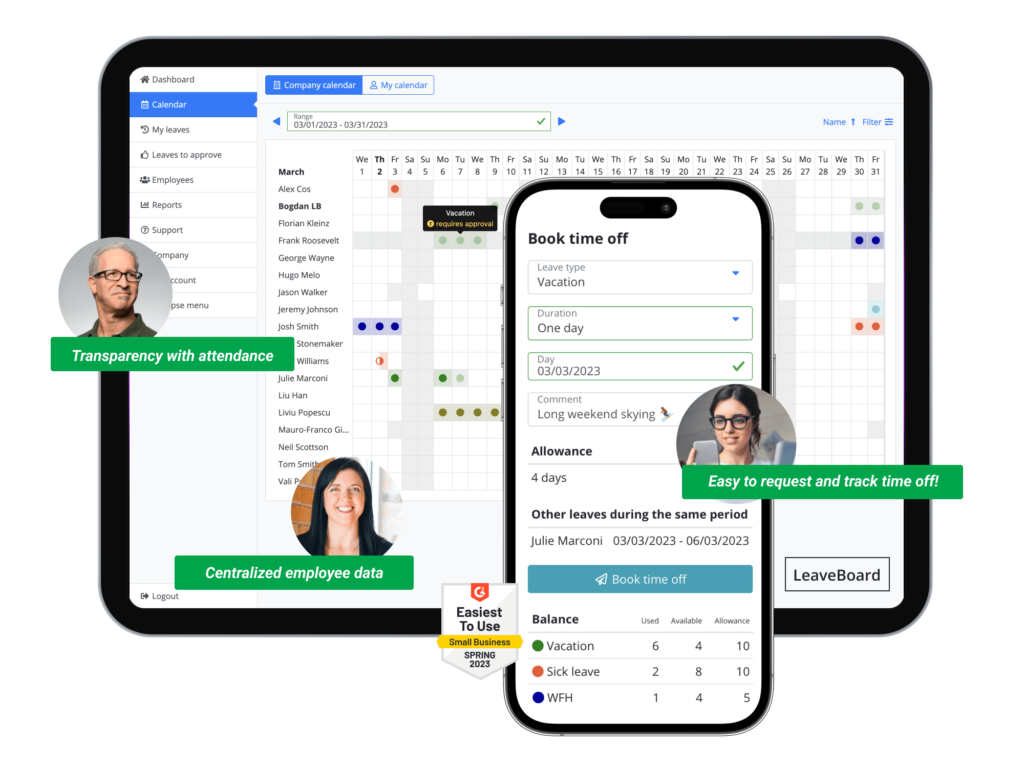
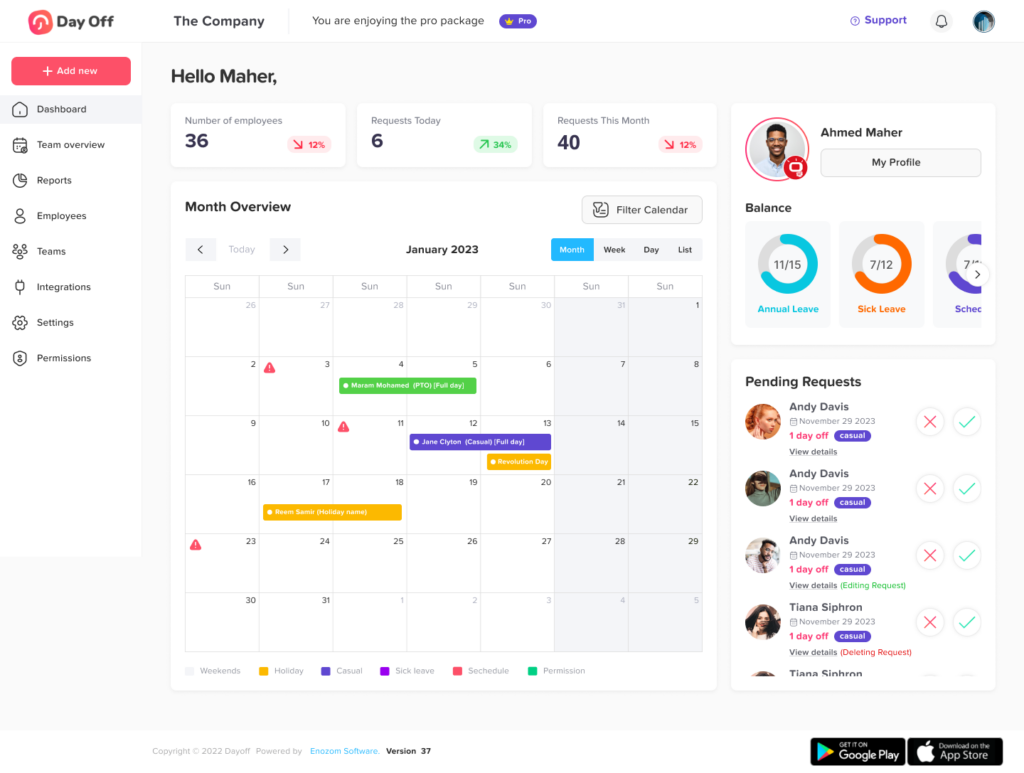
2. Real-Time Calendar Overview
One of the standout features of Day Off is its color-coded calendar view. This visual tool provides a snapshot of the team’s schedule, showing who is off and when. HR managers and team leaders can easily see which employees are taking leave on specific days, making it easier to plan and redistribute workloads. This feature also helps prevent scheduling conflicts and ensures there is adequate coverage for critical roles.
The calendar is dynamic and automatically updates with any leave approvals or changes, ensuring that both employees and managers have up-to-date information at all times.
3. Automated Leave Balances and Accruals
Gone are the days of manual leave tracking. Day Off automates leave balances, ensuring that employees and HR managers have accurate, real-time access to up-to-date leave balances. The system automatically tracks the accrual of leave based on the company’s leave policy, so there’s no need for HR staff to manually calculate or update leave balances.
Employees can view their available leave days, including any unused time from previous periods. This transparency helps prevent confusion and fosters trust between employees and management.
4. Customizable Leave Policies
Day Off is highly customizable, allowing organizations to tailor leave policies to their specific needs. This includes setting vacation accrual rates, determining carryover rules, defining the types of leave (e.g., sick leave, personal leave, or family leave), and determining approval workflows. The flexibility to customize these policies ensures that the platform fits seamlessly into any company’s existing HR processes.
HR teams can easily update or adjust leave policies, and Day Off will automatically apply these changes across all employee profiles, ensuring consistency and compliance.
5. Mobile Access for Convenience
With mobile access, Day Off brings leave management to the fingertips of employees and managers. The app is available on both iOS and Android devices, allowing employees to submit leave requests, check balances, and view the company calendar on-the-go.
For managers, mobile access means they can approve or deny leave requests quickly, without needing to be at their desk or logged into the company system. The platform’s mobile functionality makes it incredibly convenient for teams with remote workers or those working from various locations.
6. Data Insights and Reports
Day Off also features robust analytics and reporting capabilities. HR managers can generate detailed reports on employee absences, leave utilization, and trends over time. These insights help organizations understand their leave patterns, identify potential absenteeism issues, and adjust policies as necessary.
Reports can also be used for forecasting future leave requirements, helping managers plan for seasonal staffing needs or anticipated absences, and ensuring adequate coverage during peak periods.
How Day Off Can Benefit Different Organizations
Whether your company is large or small, Day Off can adapt to meet your needs. Here’s how different types of organizations can benefit:
Small Businesses: For smaller teams, the platform offers a simple and cost-effective solution to manage employee leave without overwhelming HR staff. It helps avoid scheduling conflicts and ensures that small businesses maintain operational efficiency.
Medium-Sized Enterprises: As teams grow, so do the complexities of absence management. Day Off provides scalable solutions, offering detailed reports, customizable policies, and robust mobile access to support HR teams in managing a larger workforce.
Large Corporations: For enterprises with a global or dispersed workforce, the platform’s centralized dashboard, real-time calendar, and mobile access help maintain consistency across multiple locations. The ability to manage multiple leave types and generate detailed analytics ensures that large organizations can stay compliant and efficiently manage their workforce.
Other Absence Tracking Tools
Effective absence tracking tools help businesses streamline employee time-off management, ensuring accurate records and smooth operations. Below are three top-rated solutions with their key features and potential drawbacks.
Deputy is a powerful employee scheduling and time tracking tool designed to help businesses manage shifts, attendance, and absences effortlessly. It allows employees to submit leave requests, track their availability, and access shift schedules, making it a highly efficient solution for both small and large teams. Its mobile app enables employees to manage their time off on the go, while managers can approve or reject requests in real time.
Key Features:
Leave Management: Employees can request time off, and managers can review, approve, or reject these requests in a seamless workflow.
Real-Time Scheduling: Quickly create and update schedules, accounting for absences and leave requests, minimizing conflicts.
Mobile Accessibility: Employees can request time off, view schedules, and manage their absences directly from their mobile devices.
Payroll Integration: Deputy integrates with payroll systems for smooth and accurate payment processing.
Cons:
Learning Curve: Some users report that the interface can be slightly overwhelming for first-time users, especially if the organization has complex scheduling needs.
Limited Customization for Absences: While it offers basic leave management, some businesses may find that the absence management features aren’t as customizable as they would like, especially for more complex policies.
Cost: While Deputy provides a robust feature set, it may be priced higher than some simpler alternatives, which can be a consideration for smaller businesses.
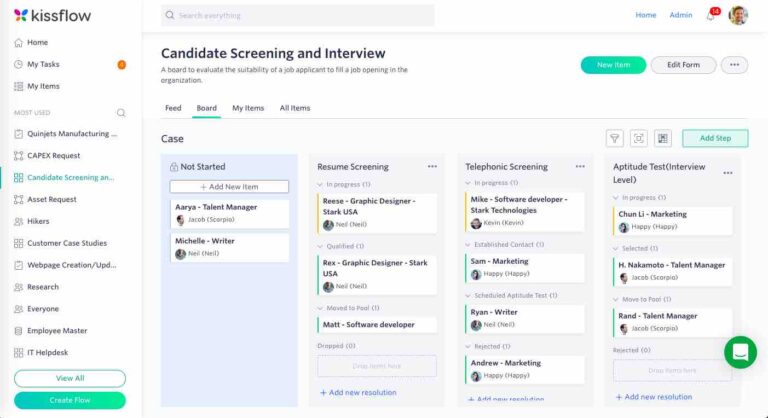
Kissflow HR Cloud is a comprehensive, cloud-based HR software platform that offers a range of HR management tools, including a sophisticated absence and leave management system. It allows for seamless absence tracking by automating leave approval workflows, making it easy for employees to submit leave requests and for HR to approve them efficiently. Kissflow’s customizable workflow templates can be adjusted to fit a company’s unique leave policies and requirements.
Key Features:
Automated Leave Approval Workflows: Kissflow automates the entire process of leave request approvals, reducing manual work and eliminating delays.
Customizable Leave Policies: You can define your own leave policies, from annual leave to sick leave, and ensure that they align with company rules.
Employee Self-Service Portal: Employees can request time off, track their leave balances, and view their absence history all in one place.
Detailed Reporting and Analytics: The tool provides managers with insightful reports and analytics to track absence trends and make informed decisions.
Cons:
Complex Setup: While Kissflow is highly customizable, setting up the tool to align perfectly with an organization’s unique leave policies can require significant time and effort.
Overkill for Small Businesses: Small businesses may find Kissflow to be more complex and feature-rich than they need, especially if they’re looking for a simple leave tracking solution.
Cost: Kissflow’s pricing can be on the higher side for smaller organizations, especially considering it provides a full suite of HR tools beyond just absence tracking.
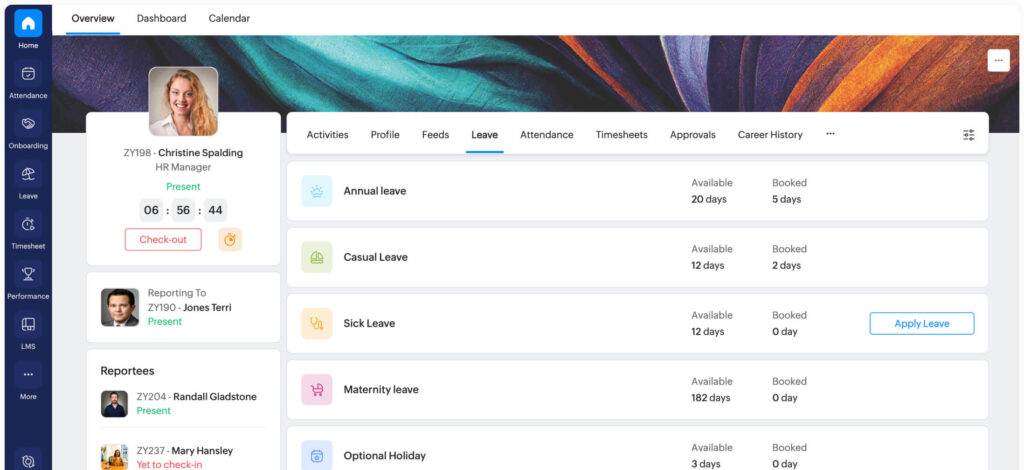
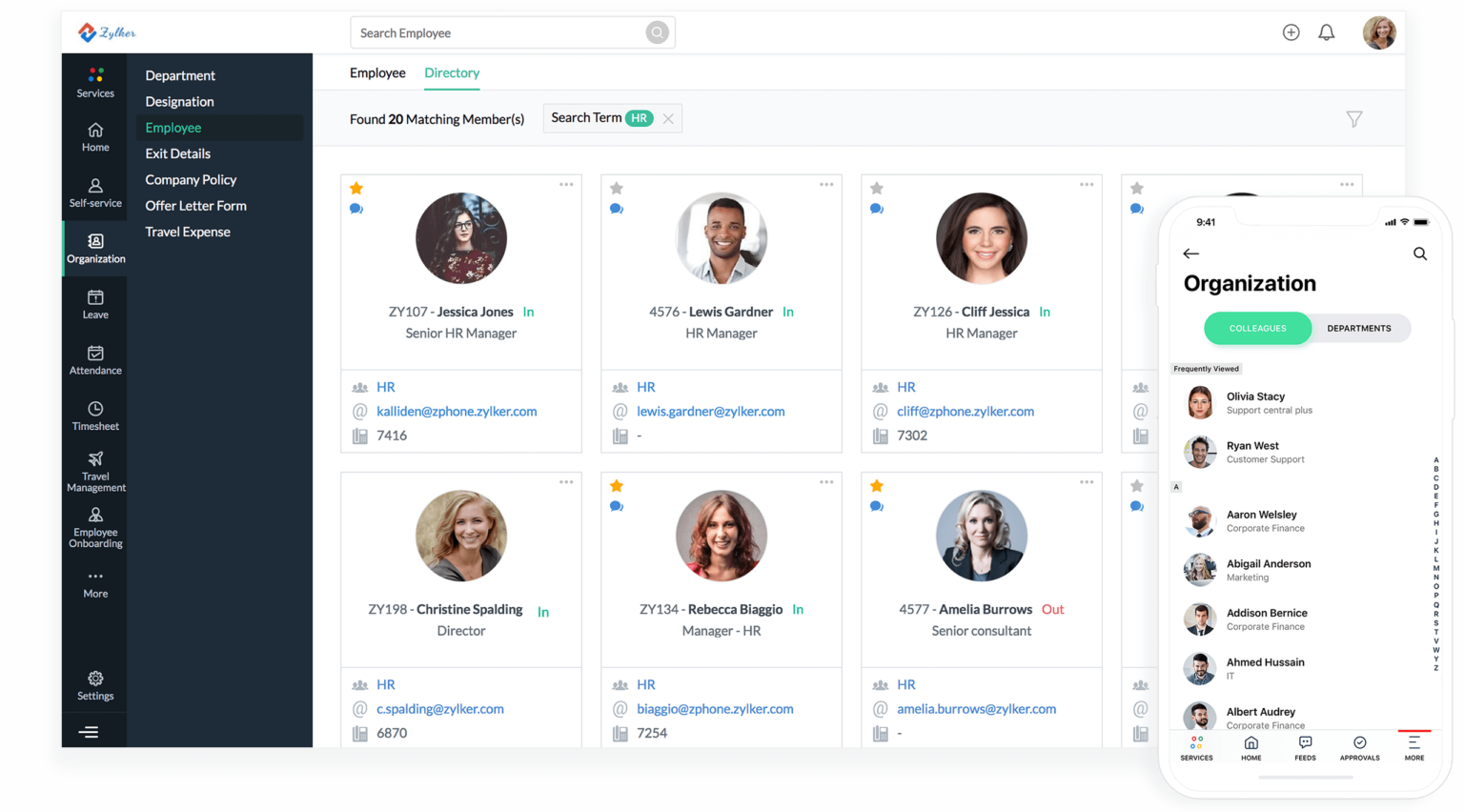
Zoho People is a cloud-based HR software that offers an intuitive absence management module. With Zoho People, HR teams can efficiently manage employee time-off requests and keep track of vacation days, sick leaves, and other absences. The platform offers customizable workflows, enabling businesses to tailor absence management according to their policies. Additionally, Zoho People integrates well with other Zoho apps, making it a great choice for businesses already using the Zoho ecosystem.
Key Features:
Customizable Leave Policies: Businesses can define various leave types and customize them to meet their specific needs.
Leave Approval Workflow: Employees can submit leave requests, and HR can approve or deny them based on preset workflows, reducing administrative overhead.
Self-Service Portal: Employees can view their leave balance, request time off, and track their absence history in one easy-to-use portal.
Integration with Payroll: Zoho People integrates seamlessly with payroll systems, ensuring accurate calculations and timely payouts.
Reporting and Analytics: The platform offers detailed reports that can provide insights into employee attendance patterns, helping HR make data-driven decisions.
Cons:
User Interface Complexity: Some users find the interface a bit cluttered and not as intuitive, especially for new users who are unfamiliar with the system.
Limited Mobile App Features: The mobile app is useful for basic functions, but it may lack some of the advanced features available on the desktop version.
Pricing: Zoho People offers various pricing tiers, but for smaller businesses or those with fewer employees, the cost might feel too steep for the features provided.
FAQ (Frequently Asked Questions)
This section answers common questions about employee absence tracking and how tools like Day Off can streamline the process. Find quick insights on best practices and optimizing your absence management.
1. What are the different types of employee absences that should be tracked?
Absences should be categorized as planned (vacation, appointments), unplanned (illness, emergencies), paid (vacation days, sick leave), unpaid (exceeding leave), and statutory (maternity/paternity, jury duty). Tracking these ensures payroll accuracy and legal compliance.
2. How can tracking employee absences improve productivity?
Absence tracking helps anticipate disruptions, redistribute workloads, and prevent bottlenecks. By knowing when key staff are absent, teams can maintain productivity, avoid overburdening employees, and ensure crucial roles are always covered.
3. Why is it important for organizations to review absence data regularly?
Regularly reviewing absence data allows HR to spot trends, optimize staffing, and ensure leave policies are effective. Identifying patterns early helps prevent issues like burnout, health concerns, or employee disengagement.
4. How can absenteeism impact an organization’s bottom line?
Absenteeism leads to lost productivity, higher overtime costs, and recruitment/training expenses. It disrupts workflows, forcing teams to work harder to compensate for the absence, which can have significant financial consequences.
5. How can absence tracking help ensure legal compliance?
Absence tracking helps ensure employees receive the right entitlements and helps companies stay compliant with labor laws, reducing the risk of legal penalties and disputes over unpaid or statutory leave.
6. How does absence tracking support employee well-being?
Tracking absences can reveal underlying health issues, burnout, or job dissatisfaction. It allows HR to offer support like wellness programs, flexible working hours, or health resources to address employee concerns proactively.
7. What are the benefits of implementing automated absence tracking systems?
Automated systems reduce errors, save time, and ensure consistency. By tracking absences in real-time, systems like Day Off allow HR to efficiently manage leave requests, approval workflows, and report generation, improving overall productivity.
8. Can absence tracking help with forecasting staffing needs?
Yes, by analyzing absence trends, HR can anticipate high absenteeism periods (e.g., holidays, flu season) and plan staffing levels accordingly, ensuring adequate coverage and preventing understaffing.
9. What is the role of absence tracking in managing absenteeism?
Absence tracking allows HR to identify frequent absenteeism, address underlying causes, and take corrective action. This helps reduce absenteeism rates, improves employee engagement, and maintains productivity.
10. How do you handle different types of leave, such as paid or unpaid leave?
Paid leave (vacation, sick days) is compensated, while unpaid leave is taken when an employee’s paid leave is exhausted. Day Off can track both types of leave, ensuring proper documentation and compliance.
11. How can I ensure confidentiality when tracking employee absences?
To maintain confidentiality, limit access to absence records, use secure systems, and ensure HR staff are trained in privacy policies. Day Off provides secure access and protects sensitive employee data.
Conclusion
In conclusion, absence tracking is more than just a tool for keeping records; it’s a strategic approach to managing workforce health and productivity. By leveraging modern absence tracking solutions, businesses can not only ensure smooth operations but also enhance employee satisfaction and engagement. Proper absence management is integral to maintaining a balanced and efficient workplace, ultimately contributing to the overall success of the organization.